

Research
and Compliance Mode note:
In RUO mode, all users can perform these tasks.
In Compliance mode, only ModFitAdmins
have permission to perform them.
This dialog is used to configure several properties of the Auto Analysis command.
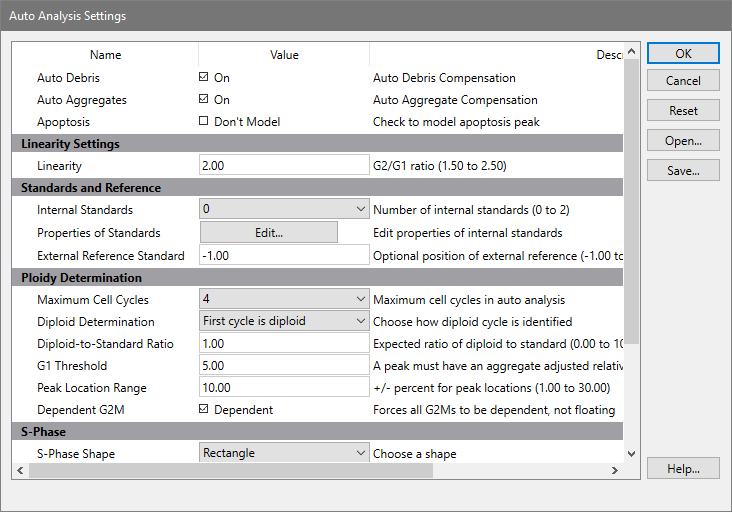
AutoDebris
When this option is checked, the program will enable the AutoDebris component to model debris in the data file during Auto Analysis. Debris is often created in the sample preparation process. If the option is not checked, the AutoDebris component will be disabled.
AutoAggregates
When this option is checked, the program will enable the AutoAggregate component to model aggregation in the data file during Auto Analysis. Aggregation in the sample can produce a continuum of particles that are stuck together, significantly affecting S-Phase estimates. If the option is not checked, the AutoAggregate component will be disabled.
Apoptosis
NOTE: We strongly recommend that this option should be disabled in your configuration. To get more robust and accurate results, use additional markers for apoptosis detection.
If this option is checked, the first peak detected after any internal standards will be considered an apoptotic population and modeled with a Gaussian.
Linearity Settings
Linearity
This value is used in the computation of some G2M positions, and in the AutoAggregate model component. The default value is 2.0, as G2M peaks are expected to appear at two times the associated G1 peak. Adjust this value to match the known linearity setting for your instrument.
When Auto Analysis does not detect a distinct G2M peak for a cycle, it assumes the location of the G2M peak to be at the G1 position times this linearity setting. This is called a dependent G2M, because its position depends on the G1.
The linearity value is used by the AutoAggregate model component to determine the expected locations of peaks created by aggregation.
Standards and References
Internal Standards
Select the number of internal standards that your data files contain.
Most DNA internal standards are designed to appear to the left of the first cycle's G1 population. By default, the program will assume that the first peaks it finds should be assigned to the number of standards you select here. Use the Properties of Standards button below to give the program additional information about the internal standards in your samples.
Properties of standards
Click this button to display the Standards dialog. This dialog allows you to edit the names and expected locations of internal standards in your samples. By entering expected locations, the program can more accurately determine which peaks are standards, and where the Diploid population occurs. See the description of Diploid determination below for more on using this value to assign ploidy.
External reference standard
If you enter a value of an external standard location, you can make use of this value in assigning ploidy labels to the cycles that AutoAnalysis finds. For example, if you run a normal Diploid control at a particular channel, you can enter that channel position in this edit box. See the description of Diploid determination below for more on using this value to assign ploidy.
Ploidy Determination
Maximum cell cycles
Select the maximum number of cell cycles that Auto Analysis can model. By default, this is set to "Unlimited". If the program detects numerous false peaks in your data files, you may want to specify a maximum of 3 or 4 cycles. See the Peak Finder Settings for more information about finding peaks.
Diploid determination
This option determines the method that Auto Analysis will use to identify the Diploid cycle in your data files.
First cycle is Diploid
This is the default selection. Use this option if you want the first (leftmost) cell cycle always to be classified as the Diploid cycle.
Based on external reference
Use this option if you have entered an expected location for an external reference above, and you want to use that position as the basis for identifying the Diploid cycle. The expected Diploid location will be computed as the External reference standard location multiplied by the Diploid-to-Standard ratio.
Based on Standard1 and Based on Standard2
Use this option if you have entered expected location(s) for internal standards above in Properties of standards, and you want to use one of the standards to compute the expected location of the Diploid cycle. The expected Diploid location will be computed as the Expected position of the standard multiplied by the Diploid-to-Standard ratio.
Examples:
1. Suppose you have one internal standard in your samples that is normally found at channel 38 in the DNA histogram, and that the normal Diploid G1 location is 1.3 times the standard's position. You would enter the expected location of the standard using Properties of standards, select Based on Standard1 for the Diploid determination option, and enter 1.3 in the Diploid-to-standard edit box.
2. Suppose you run a normal Diploid control that is positioned at channel 55 everyday, and that you expect this to be the location of Diploid cycles in your test samples as well. You would enter 55 in the External reference standard field, select Based on external reference for the Diploid determination, and enter 1.0 for the Diploid-to-Standard ratio.
Diploid-to-Standard ratio
This value is used if you have the Diploid determination option selected for Based on external reference, Based on Standard1, or Based on Standard2. The expected location for the Diploid G1 is computed by multiplying this value times the expected location of the reference or standard.
When Diploid determination is set for First cycle is Diploid, this value is not used.
G1 threshold
This value sets the minimum relative height for a peak to be considered a G1, after adjusting the height for aggregates. The relative height is a value relative to the largest peak, where the largest peak is 100%. The default setting for G1 threshold is 5%. To allow smaller peaks to be considered G1 peaks, lower the value. To make the setting more restrictive, increase the setting.
Peak location range
This value controls how much variation the program allows in looking for a peak at an expected location. It is a percentage of the expected location. If, for example, the expected location of the Diploid G1 is channel 50 and this value is set for 10%, Auto Analysis will look for a peak between channel 50 plus and minus 5 channels, or 45 to 55.
Dependent G2M
With this option enabled, Means and Standard Deviations for all G2M components will be dependent on the associated G1 components in models created by Auto Analysis. This setting creates more consistent analysis results from one operator to the next, and it is recommended. With the option disabled, any G2M component that has a well-defined Peak Finder peak will have a floating Mean and Standard Deviation. Those without well-defined peaks will be dependent on associated G1 components.
S-Phase
S-Phase shape
This option controls the mathematical function that is used to model S-Phase.
Rectangle
This is the default selection. It provides the most conservative estimate of S-Phase and is the recommended option.
Trapezoid
This option provides one additional degree of freedom over the Rectangle.
Polynomial
This option adds two degrees of freedom over a rectangle.
Number of compartments
Select the number of compartments to use in modeling S-Phase. By default, this option is 1, the recommended value.
DI for S-Phase
Enter a DNA index value (DI) below which the program will disable S-Phase modeling for the lower of two overlapping cycles. The default and recommended value is 1.3.
When two cell cycles are significantly overlapped, the S-Phases can be arbitrarily inflated or deflated in the modeling process. In this situation, it is better to disable the S-Phase for the lower-positioned cycle. The DI for S-Phase setting controls the threshold for this decision.
Tetraploid
G2M Threshold
This value determines when a peak at a G2M location is considered to be too large for a G2M peak, and is classified as a G1 peak for another cycle. The value used in making this decision is a simple statistical fit of the peak, not the modeled result for the peak.
The value is a percentage of the estimated area of the associated G1 peak. By default, the G2M can be up to 15% of its associated G1 before it is reclassified as a G1 of another cycle.
Tetraploid location range
This value controls how much variation the program allows in looking for a potential Tetraploid peak. It is a percentage of the expected location.
Open
If you have previously saved Auto Analysis settings to disk, you can use the Open button to load those settings into the program.
Save
Use this option if you want to store the current Auto Analysis settings to a file on disk. The standard file save dialog box will be displayed, allowing you to navigate to a location and name the file to save.
Reset
Click this button to restore the Auto Analysis values to the factory default settings.
OK
Click this button to accept the changes you have made and close the dialog.
Cancel
This option closes the dialog and discards any changes you might have made.
Help
This option displays the on-line help for this dialog.