Research
and Compliance Mode note:
In RUO mode, all users can perform these tasks.
In Compliance mode, only ModFitAdmins
and ModFitEditors have permission
to perform them.

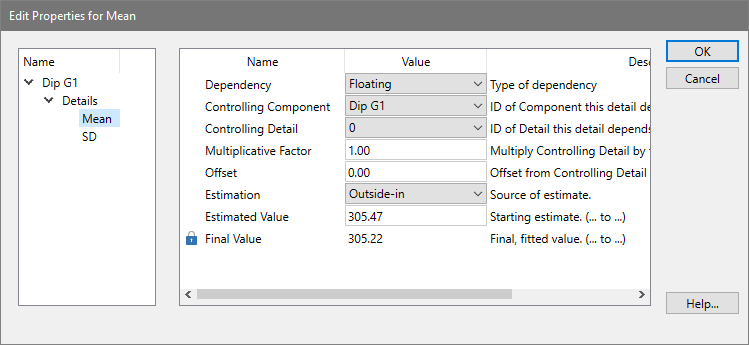
This dialog allows you to edit the properties of a model component detail. The details of a component will depend on the particular component type. The properties of each detail define how the detail is related to other component details, how it is computed, and the source of its estimates. See Edit Properties for Component for additional information.
Dependency:
This option determines how the detail is computed. Floating means that the modeling process will adjust the detail to find the best value. Floating details are commonly used for means and standard deviations of well-defined peaks modeled with Gaussian component. Dependent details are computed directly by applying a multiplicative and/or additive factor to the value of the controlling detail. Fixed details are not adjusted during the modeling process; their values are determined either by a static value or from a range estimate. Interpolate can be selected to compute the value of the detail by interpolation. It is only applicable to standard deviation details. An example best describes the use of this option. Suppose you have a model that describes a diploid population. Now suppose there is an extra peak in S-Phase that you believe should be broadened in the same way as the S-Phase is broadened. You would choose Interpolate for the standard deviation of the extra peak, and make its controlling component and detail the S-Phase lower standard deviation. The upper boundary of the interpolation is automatically the upper standard deviation.
Controlling component:
If Dependent or Interpolate is selected as the Dependency option, the controlling component determines what model component this detail is dependent upon. You must also select a Controlling detail (below) to complete the dependency. If the Dependency option is Floating or Fixed, the controlling component is ignored.
Controlling detail:
If Dependent or Interpolate is selected as the Dependency option, the controlling detail determines the detail of the Controlling Component on which this detail depends. If the Dependency option is Floating or Fixed, the controlling component is ignored.
Multiplicative factor:
If Dependent is selected as the Dependency option, the final value of the controlling component's detail is multiplied by the multiplicative factor. As an example, the G2M component's mean position is often made dependent on the G1 component's mean by a factor of 2.
Offset:
If Dependent is selected as the Dependency option, this value is added to the final value of the controlling component's detail, after it has been multiplied by the multiplicative factor.
Estimation:
This drop down provides choices for the source of the estimate for the detail. Outside-in and Inside-out draw the estimate from simple statistics performed before the modeling process. Range draws the estimate from a range associated with this component. User-entered estimate uses the value entered in the Estimated value field as the source of the estimate.
Estimated value:
This field displays the estimate that was used for the detail when the model was last run. If Estimation is set to User-entered estimate, the value will not be adjusted. In all other cases, the value may change each time you choose Fit, depending on how the details dependencies are set.
Final value:
This read-only field displays the result of the last modeling process for this model.
OK:
Click this button to accept the changes and close the dialog.
Cancel:
Click this button to cancel changes and close the dialog. This button may be disabled if changes are made that cannot be cancelled.
Help
Click this button to display online help for this topic.